Why Ball Valves are the Best Choice for Gases?
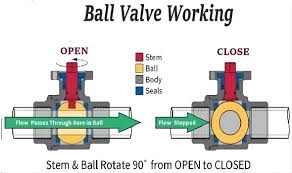
The Application of Ball Valves
When it comes to ball valves for gas, Cameron stands out as a reliable brand in the industry. These valves, particularly ball valves for natural gas, play a pivotal role in various industrial applications. Designed to withstand high pressure, they ensure efficient control and safety in critical operations. Apollo ball valves for natural gas are renowned for their durability and precision engineering, making them a preferred choice in the market. Whether in oil and gas, petrochemical, or manufacturing industries, these valves excel in regulating the flow of gases with utmost reliability. From controlling the flow in pipelines to managing processes in refineries, ball valves are indispensable for ensuring smooth operations and safety. With Cameron’s expertise and innovation, these valves continue to set the standard for excellence in the field.
What Are The Types Of Ball Valves?
- Floating Ball Valve: In this type, the ball is not fixed to the stem but floats slightly, allowing it to move with the flow pressure. This design reduces operating torque and enhances sealing performance.
- Trunnion Ball Valve: Unlike floating ball valves, trunnion ball valves have a fixed ball supported by trunnions. This design is suitable for high-pressure and large-diameter applications, providing more stability and better sealing performance.
- Three-Way Ball Valve: Three-way ball valves have three ports, allowing them to control the flow between multiple pipes or directions. They are often used for diverting, mixing, or isolating flow in complex piping systems.
- V Port Ball Valve: V port ball valves have a V-shaped ball, which enables them to provide more precise control over the flow rate. They are commonly used in applications requiring accurate modulation, such as in chemical processing or HVAC systems.
- Cavity Filler Ball Valve: These ball valves feature a cavity filled with a material like PTFE (Teflon) to prevent fluid buildup and ensure smooth operation, making them suitable for handling viscous or sticky fluids.
Why Ball Valves are the Best Choice for Gases?
- Quick Operation: Ball valves offer fast and reliable operation, allowing for rapid opening and closing with a simple 90-degree turn of the handle or actuator. This feature is crucial in emergency shutdown situations or when swift flow control is needed.
- Tight Shutoff: Ball valves provide excellent sealing capabilities, ensuring tight shutoff and minimal leakage even at high pressures. This characteristic is essential for maintaining the integrity of gas systems and preventing wastage or environmental hazards.
- Versatility: Ball valves are versatile and can handle a wide range of gases, including natural gas, propane, methane, and others. They are suitable for various industrial applications across different sectors, from oil and gas to chemical processing and HVAC systems.
- Durability: Constructed from robust materials such as stainless steel, brass, or carbon steel, ball valves exhibit high durability and resistance to corrosion, erosion, and wear. This durability ensures long-term reliability and minimal maintenance requirements, even in harsh operating environments.
- Compact Design: Ball valves have a compact design, making them space-efficient and easy to install in tight or confined spaces. This feature is advantageous in industrial facilities where space optimization is crucial.
What Is Ball Valves?
Ball valves are mechanical devices used to control the flow of fluids in pipelines. They consist of a spherical ball with a hole through its center, which rotates to either allow or block the flow of fluid. When the hole aligns with the pipeline, fluid can pass through, and when perpendicular, it stops flow. This simple yet effective design makes ball valves popular for their reliability and versatility in various industries.
How Does Ball Valves work?
Ball valves operate by rotating a spherical ball with a hole in the center within a valve body. When the ball is aligned with the pipeline, fluid can flow through the hole. Rotating the ball 90 degrees blocks the flow by positioning the solid part of the ball against the pipeline, effectively sealing it off. This simple mechanism allows for quick and precise control of fluid flow.
Features of Ball Valves
- Versatility: Ball valves are suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential plumbing to industrial processes, thanks to their ability to handle various fluids, including gases and liquids.
- Quick Operation: With a simple 90-degree turn, ball valves can swiftly open or close, facilitating rapid flow control. This feature is particularly useful in emergency situations or when immediate shut-off is necessary.
- Tight Sealing: The design of ball valves ensures tight sealing, minimizing leakage and preventing fluid loss or contamination. This characteristic is crucial for maintaining system integrity and safety.
- Durability: Constructed from robust materials such as stainless steel or brass, ball valves exhibit high durability and resistance to corrosion, erosion, and wear. They can withstand harsh operating conditions, ensuring long-term reliability.
- Compact Design: Ball valves have a compact and lightweight design, making them easy to install even in confined spaces. Their space-saving nature enhances versatility and facilitates installation in various environments.
Advantages of Ball Valves
- Quick Operation: Ball valves offer rapid opening and closing, enabling efficient flow control with minimal effort.
- Excellent Sealing: The design of ball valves ensures tight sealing, reducing the risk of leaks and ensuring system integrity.
- Versatility: They can handle a wide range of fluids, including gases and liquids, making them suitable for diverse applications.
- Durability: Constructed from sturdy materials like stainless steel or brass, ball valves are highly durable and resistant to corrosion and wear.
- Minimal Maintenance: Due to their robust construction and simple design, ball valves require little maintenance, reducing downtime and operating costs.
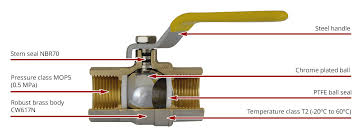
The Specifications of Ball Valves
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Ball Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel |
| Attachment Type | Threaded |
| Thread Standard | NPT (National Pipe Thread) |
| Thread Size | 1/2 inch |
| Body Material | Brass |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Air, Oil, Gas |
| Handle Type | Lever |
| Handle Material | Aluminum |
| Maximum Working Pressure psi | 600 psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure bar | 41.4 bar |
| Operating Pressure | 0-400 psi |
The Installation Steps for Ball Valves
- Preparation:
- Gather necessary tools and equipment, including pipe wrenches, pipe sealant, and Teflon tape.
- Ensure the valve and pipes are clean and free from debris.
- Select Valve Position:
- Determine the desired location for the valve in the pipeline.
- Ensure the valve handle can be easily accessed for operation.
- Shut Off Supply:
- Close the main supply valve to stop the flow of fluid in the pipeline.
- Release any pressure in the system by opening faucets or relief valves.
- Measure and Cut Pipe:
- Measure and mark the pipe at the installation point according to the valve size.
- Use a pipe cutter to cut the pipe cleanly and squarely.
- Prepare Valve and Pipes:
- Apply pipe sealant or Teflon tape to the threaded ends of the valve and pipes.
- Ensure the valve is in the closed position before installation.
- Attach Valve to Pipes:
- Thread the valve onto the pipe ends by hand, ensuring a snug fit.
- Use pipe wrenches to tighten the connections securely, taking care not to over-tighten and damage the threads.
- Test for Leaks:
- Slowly open the main supply valve to allow fluid into the system.
- Check all connections for leaks by applying a soapy water solution and looking for bubbles.
- Tighten any connections if leaks are detected.
- Finalize Installation:
- Once all connections are leak-free, operate the valve to ensure proper functionality.
- Securely anchor the valve to nearby structures or supports if necessary.
- Label the valve for easy identification and future maintenance.
The Operation Theory of Ball Valves
- Principle:
- Ball valves control the flow of fluids through a hollow, perforated sphere (the “ball”) within the valve body.
- When the ball’s hole is aligned with the pipeline, fluid can pass through, and when turned perpendicular, it blocks the flow.
- Gas Line Application:
- In gas line systems, ball valves regulate the flow of gas, ensuring safety and efficient distribution.
- When open, gas flows freely through the valve, and when closed, it stops the gas flow entirely.
- Gas Pipeline Application:
- In gas pipelines, ball valves serve as crucial control points for managing gas transmission and distribution.
- They enable operators to isolate sections of the pipeline for maintenance or emergency shutdowns.
- Safety Considerations:
- Ball valves for gas lines and pipelines must meet stringent safety standards to prevent leaks and ensure reliable operation.
- Proper installation, regular maintenance, and periodic inspection are essential to uphold safety and performance.
- Advantages:
- Ball valves offer quick and precise flow control, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid shut-off or modulation.
- Their tight sealing capabilities minimize leakage, enhancing safety and efficiency in gas systems.
The Parameters Table of Ball Valves
| Parameter | Material |
|---|---|
| Body | Stainless Steel, Brass, Carbon Steel, Cast Iron, PVC, etc. |
| Ball | Stainless Steel, Brass, Chrome-plated Brass, Bronze, etc. |
| Stem | Stainless Steel, Nickel-plated Brass, Aluminum Bronze, etc. |
| Seat | PTFE (Teflon), Nylon, Delrin, Peek, etc. |
| Seals/O-rings | Nitrile (Buna-N), Viton, EPDM, Silicone, etc. |
| Handle | Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Plastic, etc. |
| Bonnet | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Brass, etc. |
| Bolts/Nuts | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Brass, etc. |
| Gaskets | PTFE (Teflon), Graphite, Rubber, etc. |



