Cryogenic Valves – Uses, Types, Standards, and Testing

The Application of Cryogenic Valves
Introducing Cameron’s cutting-edge cryogenic valves, designed to excel in low-temperature environments. From cryogenic ball valves to cryogenic solenoid valves, our products boast robust construction and precision engineering, ensuring reliable operation in extreme cold conditions. Ideal for applications in industries such as aerospace, medical, and liquefied natural gas (LNG) processing, Cameron’s cryogenic valves offer exceptional performance and durability. With a focus on quality and innovation, Cameron delivers superior solutions to meet the unique demands of cryogenic processes. Trust Cameron for dependable cryogenic valve solutions that ensure safety and efficiency in your operations.
What Are The Types Of Cryogenic Valves?
- Cryogenic Ball Valves: These valves feature a rotating ball with a bore through it to control flow. They offer tight shut-off and are suitable for high-pressure and high-flow applications.
- Cryogenic Gate Valves: Gate valves have a sliding gate or wedge that controls flow by moving up and down. They provide a tight seal and are often used in applications requiring full flow or minimal pressure drop.
- Cryogenic Globe Valves: Globe valves have a disc that moves perpendicular to the flow direction to regulate fluid flow. They offer precise control and are commonly used in throttling applications.
- Cryogenic Butterfly Valves: Butterfly valves feature a disc that rotates around a central axis to control flow. They offer quick operation and are suitable for large-diameter pipelines.
- Cryogenic Solenoid Valves: Solenoid valves use an electromechanical solenoid to control the flow of cryogenic fluids. They are often used for on/off control in automated systems.
What Is Cryogenic Valves?
Cryogenic valves are specially designed valves capable of withstanding and operating effectively in extremely low-temperature environments. These valves are engineered to handle cryogenic fluids such as liquefied natural gas (LNG), liquid nitrogen, and liquid oxygen, which are stored and transported at temperatures below -150°C (-238°F). Cryogenic valves are constructed with materials that can maintain their integrity and functionality in these harsh conditions, ensuring reliable fluid control and preventing leakage or failure. They play a crucial role in industries such as aerospace, medical, LNG processing, and industrial gas storage and transportation, where precise fluid control at cryogenic temperatures is essential for safe and efficient operations.
How to Select the Right Cryogenic Valves?
When selecting the right cryogenic valves, consider factors such as the type of cryogenic fluid, temperature range, pressure requirements, flow rate, and compatibility with the application environment.
Features of Cryogenic Valves
- Low-Temperature Performance:
- Cryogenic valves are specifically designed to maintain functionality and integrity in extremely low-temperature environments, ensuring reliable operation even at temperatures below -150°C (-238°F).
- Materials:
- Constructed from specialized materials such as stainless steel, brass, or bronze, which offer excellent corrosion resistance and maintain mechanical properties at cryogenic temperatures.
- Tight Sealing:
- Designed to provide tight sealing to prevent leakage of cryogenic fluids, ensuring safety and efficiency in cryogenic applications.
- Extended Bonnet:
- Many cryogenic valves feature an extended bonnet design to protect the stem and packing from the low temperatures, minimizing the risk of stem freezing and ensuring smooth operation.
- Low Thermal Conductivity:
- The materials used in cryogenic valves have low thermal conductivity, reducing heat transfer from the surrounding environment and minimizing the risk of frost formation or ice buildup on the valve.
- Fire-Safe Design:
- Some cryogenic valves are equipped with fire-safe features to ensure reliable operation in the event of a fire, providing added safety in critical applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cryogenic Valves
Advantages:
- Reliable Performance: Cryogenic valves are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and maintain reliable performance in low-temperature environments.
- Safety: These valves offer tight sealing to prevent leakage of cryogenic fluids, ensuring safe handling and operation.
- Diverse Applications: Cryogenic valves are versatile and find applications in various industries such as aerospace, medical, LNG processing, and industrial gas storage and transportation.
Disadvantages:
- Specialized Design: Cryogenic valves require specialized design and materials to withstand low temperatures, which can increase manufacturing costs.
- Maintenance: Due to their specialized construction, cryogenic valves may require more frequent maintenance and inspection to ensure proper functioning in cryogenic environments.
- Limited Compatibility: Cryogenic valves may have limited compatibility with certain fluids or applications, requiring careful selection to ensure suitability for specific requirements.
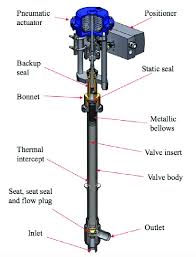
The Specifications of Cryogenic Valves
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Cryogenic Valve |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, Carbon Steel, etc. |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, etc. |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, Socket Weld, etc. |
| Thread Standard | NPT, BSPT, BSPP, DIN, JIS, etc. |
| Thread Size | 1/4 inch – 12 inches (or as per specification) |
| Safe for Use With | Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), Liquid Nitrogen, Liquid Oxygen, etc. |
| Handle Type | Lever, Gear Operated, Actuated, etc. |
| Handle Material | Stainless Steel, Aluminum, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | Up to 6000 psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | Up to 413.68 bar |
| Operating Pressure | Depends on the maximum working pressure and application requirements |
The Installation Steps for Cryogenic Valves
- Preparation:
- Gather all necessary tools and equipment, including wrenches, gaskets, and pipe thread sealant.
- Ensure the work area is well-ventilated and free from any potential hazards.
- Valve Positioning:
- Identify the optimal location for the cryogenic valve within the pipeline, considering accessibility and flow direction.
- Valve Orientation:
- Ensure the valve is installed in the correct orientation, with the flow direction indicated by the arrow on the valve body.
- Attachment Connection:
- Connect the cryogenic valve to the piping system using the appropriate attachment type, such as flanged or threaded connections.
- Apply pipe thread sealant or gaskets to ensure a secure seal.
- Alignment:
- Align the cryogenic valve with the pipeline to ensure proper installation and operation.
- Use alignment tools or shims as needed to achieve the desired alignment.
- Tightening:
- Securely tighten the bolts or nuts on the valve flanges to ensure a leak-free connection.
- Follow the manufacturer’s specifications for torque requirements.
- Pressure Testing:
- Conduct a pressure test on the cryogenic valve and piping system to ensure there are no leaks or defects.
- Gradually increase pressure and monitor for leaks, following industry-standard procedures.
- Insulation:
- Install appropriate insulation around the cryogenic valve and piping to minimize heat transfer and maintain low temperatures.
- Use insulation materials suitable for cryogenic applications, such as foam or fiberglass.
- Final Inspection:
- Inspect the installed cryogenic valve for proper alignment, tightness of connections, and overall functionality.
- Verify that all components are installed correctly and securely.
- Documentation:
- Maintain detailed records of the installation process, including valve specifications, pressure test results, and any adjustments made during installation.
- Update system documentation and diagrams to reflect the newly installed cryogenic valve.
The Operation Theory of Cryogenic Valves
- Cryogenic Ball Valves:
- These valves feature a spherical closure mechanism (the ball) with a hole through it.
- When the valve is open, the ball rotates to align the hole with the flow path, allowing fluid to pass through.
- To close the valve, the ball is rotated perpendicular to the flow, blocking the passage of fluid.
- Cryogenic Check Valves:
- Cryogenic check valves are designed to allow fluid flow in one direction while preventing backflow.
- They typically feature a swinging disc or a spring-loaded disc that moves freely in response to fluid pressure.
- When fluid flows in the desired direction, the disc moves away from the valve seat, allowing flow to continue.
- If flow reverses, the disc quickly moves back into position, sealing the valve and preventing backflow.
The Parameters Chart of Cryogenic Valves
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Valve Type | Cryogenic Valve |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, Carbon Steel, etc. |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, etc. |
| Seat Material | PTFE, Reinforced PTFE, PCTFE, etc. |
| Stem Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, etc. |
| Packing Material | PTFE, Graphite, etc. |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, Socket Weld, etc. |
| Connection Standard | ANSI, API, DIN, JIS, BS, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | Up to 6000 psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | Up to 413.68 bar |
| Operating Temperature | -196°C to 120°C (-320°F to 248°F) or as per specification |