Valve Bonnet – Types, Leakages, and Repair
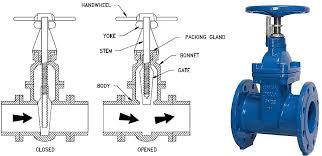
The Application of Valve Bonnet
Introducing the valve bonnet, a critical component in valve assemblies, including long bonnet ball valves and other types. As a leading manufacturer, Cameron provides innovative solutions in valve technology. The bonnet serves as the cover for the valve body, providing protection and access to internal components. It ensures a tight seal, preventing leakage and maintaining system integrity. The design of the bonnet varies depending on the valve type and application, with options for bolted, threaded, or welded connections. In addition to sealing, bonnets may also incorporate features for temperature control, insulation, and pressure relief. Overall, the valve bonnet plays a crucial role in the reliable operation of various valves across industries.
valve bonnet types
bonnet types
what is a valve bonnet
valve bonnets
cameron gate valve
control valve bonnet types
What Are The Types Of Valve Bonnet?
- Bolted Bonnet: This type of bonnet is secured to the valve body using bolts, providing a tight seal and easy access to internal components for maintenance.
- Welded Bonnet: In welded bonnet valves, the bonnet is welded directly to the valve body, creating a permanent seal and enhancing structural integrity.
- Pressure Seal Bonnet: Pressure seal bonnets are designed for high-pressure applications, featuring a self-sealing mechanism that becomes tighter as pressure increases.
- Integral Bonnet: Integral bonnets are machined as part of the valve body, eliminating the need for separate bonnet components and reducing potential leakage points.
- Screwed Bonnet: Screwed bonnets use threaded connections to secure the bonnet to the valve body, offering a simple and cost-effective sealing solution.
- Union Bonnet: Union bonnets utilize union connections to attach the bonnet to the valve body, facilitating quick disassembly and reassembly for maintenance purposes.
What Is Valve Bonnet?
Valve bonnet serves as a protective cover for the internal components of a valve, such as the valve plug or transformers. It ensures a tight seal, preventing leakage and maintaining system integrity. The design of the bonnet varies depending on the valve type and application, with options for bolted, welded, or pressure seal configurations. Typically, it provides easy access to the valve internals for maintenance while withstanding the operating pressures and temperatures of the system. Overall, the valve bonnet is crucial for the reliable operation of various valves across industries.
How Does Valve Bonnet?
Valve bonnet functions as a protective cover for a valve’s internal components. It seals tightly against the valve body to prevent leakage and maintain system integrity. Depending on the type, it may attach using bolts, welding, or pressure seals. Its design allows for easy access to the valve internals for maintenance while withstanding the pressures and temperatures of the system. Overall, the valve bonnet ensures the reliable operation of valves across various industries.
Features of Valve Bonnet
- Sealing: The primary feature of a valve bonnet is its ability to create a tight seal against the valve body, preventing leakage and maintaining system integrity.
- Accessibility: It allows easy access to the valve internals for inspection, maintenance, and repair, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
- Variety: There are various types of valve bonnets available, including bolted, welded, pressure seal, integral, screwed, and union bonnets, catering to different application requirements.
- Compatibility: The design of the bonnet ensures compatibility with different valve types, sizes, and pressure ratings, providing versatility in application.
- Durability: Constructed from robust materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel, valve bonnets are durable and resistant to corrosion and wear.
- Pressure and Temperature Resistance: It is designed to withstand the operating pressures and temperatures of the system, ensuring reliable performance in harsh environments.
- Safety: By securely sealing the valve internals, the bonnet enhances safety by preventing fluid leaks and minimizing the risk of accidents.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Valve Bonnet
Advantages:
- Leak Prevention: Valve bonnets provide a tight seal, preventing fluid leakage and ensuring system integrity.
- Accessibility: They allow for easy access to valve internals for inspection, maintenance, and repair, facilitating efficient operation.
- Versatility: With various types available, including bolted, welded, and pressure seal bonnets, they offer versatility to suit different application requirements.
- Compatibility: Valve bonnets are compatible with different valve types, sizes, and pressure ratings, providing flexibility in application.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Some types of valve bonnets, such as pressure seal or welded bonnets, may require more intricate installation procedures and specialized equipment.
- Cost: Certain types of valve bonnets, particularly those with advanced sealing mechanisms or materials, may incur higher costs compared to simpler designs.
- Maintenance: While valve bonnets allow for easy access to internals, they may require periodic maintenance to ensure proper sealing and functionality, adding to maintenance costs and downtime.
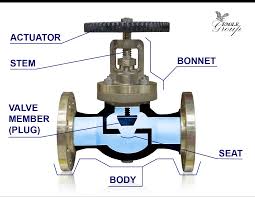
The Specifications of Valve Bonnet
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, PVC, etc. |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, Grooved, etc. |
| Thread Standard | ANSI B1.20.1, BSPT, NPT, etc. |
| Thread Size | 1/2 inch, 3/4 inch, 1 inch, etc. |
| Body Material | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, PVC, etc. |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Oil, Gas, Steam, Chemicals, etc. |
| Handle Type | Handwheel, Lever, Gear Operator, Electric Actuator, Pneumatic Actuator, etc. |
| Handle Material | Steel, Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Plastic, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | 150 psi, 300 psi, 600 psi, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | 10.3 bar, 20.7 bar, 41.4 bar, etc. |
| Operating Pressure | 0-100 psi, 0-200 psi, 0-400 psi, etc. |
The Installation Steps for Valve Bonnet
- Preparation: Gather all necessary tools and equipment, including wrenches, bolts, nuts, and any specialized tools required for the specific valve and installation environment.
- Inspection: Thoroughly inspect the valve body, bonnet, gaskets, and other components for any signs of damage or defects before installation.
- Cleaning: Clean the valve body and bonnet surfaces to remove any dirt, debris, or residues that may interfere with the sealing process.
- Alignment: Ensure proper alignment of the valve bonnet with the valve body, ensuring that bolt holes or other attachment points are correctly aligned.
- Attachment: Securely attach the valve bonnet to the valve body using bolts, welding, or other appropriate methods, following the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications.
- Sealing: Install gaskets or sealing materials as required between the bonnet and valve body to ensure a tight seal and prevent leakage.
- Tightening: Gradually tighten the bolts or fasteners in a crisscross pattern to evenly distribute the load and achieve the recommended torque.
- Final Checks: Perform a visual inspection of the installed bonnet to ensure it is properly aligned, securely attached, and sealed against the valve body.
- Testing: Conduct a pressure test to verify the integrity of the seal and ensure that the valve operates smoothly without any leaks or issues.
- Documentation: Record the installation details, including torque values, pressure test results, and any other relevant information for future reference.
The Operation Theory of Valve Bonnet
- Sealing Mechanism: The primary function of a valve bonnet is to seal the space between the valve body and its internal components, such as the gate in gate valves. This prevents fluid leakage and ensures the integrity of the system.
- Pressure Containment: The bonnet is designed to withstand the pressure exerted by the fluid flowing through the valve. In gate valves, the bonnet helps contain the pressure within the valve body, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
- Access Point: While sealing the valve, the bonnet also serves as an access point for maintenance and repair. In gate valves, the bonnet can be removed to access the gate and other internal components for inspection or servicing.
- Variety of Designs: Bonnets come in various designs to suit different types of valves and applications. For example, gate valve bonnets may feature bolted, welded, or pressure seal configurations, each offering specific advantages in terms of sealing and maintenance.
- Material Compatibility: Bonnets are typically made from materials compatible with the fluids and operating conditions of the system. This ensures durability and longevity, even in harsh environments.
The Parameters Chart of Valve Bonnet
| Parameter | Material Options |
|---|---|
| Bonnet Type | Bolted, Welded, Pressure Seal, Integral, Screwed, Union |
| Bonnet Material | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Brass, etc. |
| Seal Material | Graphite, PTFE, Rubber, Nitrile, Viton, etc. |
| Gasket Material | Graphite, PTFE, Rubber, Nitrile, Viton, etc. |
| Bolt and Nut Material | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Brass, etc. |