Plug Valves – Types, Construction, and Applications
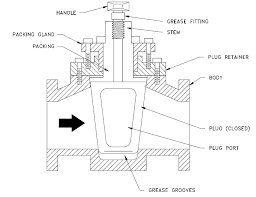
The Application of Plug Valves
Introducing Plug valves, essential components in fluid control systems, including oil drain plug valve and Durco plug valve. As a leading manufacturer, Cameron offers a diverse range of plug valves tailored to various industries. These valves feature a cylindrical or tapered plug that rotates within the valve body to control flow. They are commonly used in applications requiring tight shut-off and low-pressure drop. Plug valves are well-suited for handling abrasive and corrosive fluids due to their simple design and robust construction. They find extensive use in oil and gas, chemical processing, wastewater treatment, and other industrial applications where reliable and efficient flow control is essential.
What Are The Types Of Plug Valves?
- Tapered Plug Valves: These valves feature a tapered plug that fits snugly into the valve seat, providing a tight seal when closed.
- Lubricated Plug Valves: Lubricated plug valves have a lubricant injected between the plug and the body to reduce friction and improve sealing performance.
- Non-Lubricated Plug Valves: Non-lubricated plug valves do not require external lubrication, making them suitable for applications where contamination from lubricants must be avoided.
- Sleeved Plug Valves: Sleeved plug valves feature a flexible sleeve around the plug, providing excellent sealing performance even in abrasive or corrosive environments.
- Eccentric Plug Valves: Eccentric plug valves have a plug offset from the centerline of the valve body, allowing for bubble-tight shut-off and reduced wear on the sealing surfaces.
What Is Plug Valves?
Plug valves are essential components in fluid control systems, featuring a cylindrical or tapered valve plug that rotates within the valve body to regulate flow. These valves offer excellent shut-off capabilities and low-pressure drop, making them ideal for a wide range of applications. With their simple design and reliable performance, plug valves are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment. They play a crucial role in controlling the flow of various liquids and gases, ensuring efficient and safe operation of industrial processes.
How Does Plug Valves?
Plug valves operate by rotating a cylindrical or tapered valve plug within the valve body to control the flow of fluids. When the plug is in the open position, fluid can flow through the valve. Rotating the plug to the closed position blocks the flow, providing a tight shut-off. This simple but effective mechanism makes plug valves suitable for a wide range of applications where reliable shut-off is essential, such as in oil and gas pipelines, chemical processing, and water treatment plants.
Features of Plug Valves
- Tight Shut-off: Plug valves offer excellent sealing capabilities, providing a tight shut-off to prevent leakage and ensure system integrity.
- Low Pressure Drop: Due to their streamlined flow path, plug valves minimize pressure drop across the valve, optimizing system efficiency.
- Versatility: These valves are suitable for handling a wide range of fluids, including liquids, gases, and slurries, making them versatile for various applications.
- Abrasion Resistance: Some plug valves feature a sleeved design or special coatings to resist abrasion, extending valve life in abrasive media.
- Simple Design: With fewer moving parts, plug valves have a simple design, reducing maintenance requirements and enhancing reliability.
- Quick Operation: Plug valves can be operated quickly with a quarter-turn of the handle or actuator, allowing for rapid shut-off or flow adjustment.
- Bubble-tight Seal: When closed, plug valves provide a bubble-tight seal, ensuring zero leakage and maintaining system integrity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Plug Valves
Advantages:
- Excellent Shut-off: Plug valves offer tight sealing capabilities, providing reliable shut-off to prevent leakage.
- Low Pressure Drop: Due to their streamlined flow path, plug valves minimize pressure drop across the valve, optimizing system efficiency.
- Versatility: These valves are suitable for handling a wide range of fluids, including liquids, gases, and slurries, making them versatile for various applications.
- Simple Design: With fewer moving parts, plug valves have a simple design, reducing maintenance requirements and enhancing reliability.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Control: Plug valves typically offer limited control over flow rates compared to other valve types like globe or butterfly valves.
- Potential for Cavitation: In high-pressure applications, plug valves may be susceptible to cavitation, leading to erosion and damage over time.
- Limited in Size: Plug valves are generally available in smaller sizes, limiting their applicability in larger pipeline systems.
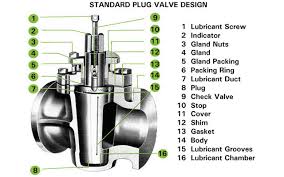
The Specifications of Plug Valves
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | Plug Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, PVC, etc. |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, Grooved, etc. |
| Thread Standard | ANSI B1.20.1, BSPT, NPT, etc. |
| Thread Size | 1/2 inch, 3/4 inch, 1 inch, etc. |
| Body Material | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, PVC, etc. |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Oil, Gas, Steam, Chemicals, etc. |
| Handle Type | Handwheel, Lever, Gear Operator, Electric Actuator, Pneumatic Actuator, etc. |
| Handle Material | Steel, Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Plastic, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | 150 psi, 300 psi, 600 psi, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | 10.3 bar, 20.7 bar, 41.4 bar, etc. |
| Operating Pressure | 0-100 psi, 0-200 psi, 0-400 psi, etc. |
The Installation Steps for Plug Valves
- Preparation: Gather all necessary tools and equipment, including wrenches, bolts, nuts, and any specialized tools required for the specific valve and installation environment.
- Shut Off System: Ensure the system where the plug valve will be installed is completely shut off and depressurized to prevent accidents.
- Positioning: Place the plug valve in the desired location within the pipeline, ensuring proper alignment with the existing piping system.
- Attachment: Securely attach the plug valve to the pipeline using appropriate fittings, flanges, or welding methods, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Connection: Connect the plug valve to the adjacent piping system using suitable gaskets, bolts, and nuts, ensuring a tight and leak-free connection.
- Testing: Conduct a pressure test to ensure the plug valve and connections are properly sealed and capable of withstanding the system’s operating pressure.
- Operation Check: Verify that the plug valve operates smoothly by manually opening and closing it several times, checking for any signs of binding or obstruction.
- Final Checks: Inspect the entire installation for any leaks, loose connections, or irregularities, and address any issues before putting the system into service.
The Operation Theory of Plug Valves
- DeZURIK Plug Valves: These valves feature a cylindrical or tapered plug that rotates within the valve body to control flow. The plug is typically equipped with a PTFE or elastomer sleeve to provide a tight seal against the valve body.
- Eccentric Plug Valves: Eccentric plug valves have a plug offset from the centerline of the valve body, allowing for bubble-tight shut-off and reduced wear on the sealing surfaces. This design minimizes friction and ensures smooth operation.
The Parameters Chart of Plug Valves
| Parameter | Material Options |
|---|---|
| Valve Type | Plug Valve |
| Plug Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, PVC, etc. |
| Body Material | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, PVC, etc. |
| Sleeve Material | PTFE, EPDM, Nitrile, Viton, Neoprene, etc. |
| Stem Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Brass, Bronze, etc. |
| Seals | PTFE, EPDM, Nitrile, Viton, Neoprene, etc. |
| Seat Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, PTFE, etc. |
| Bolts and Nuts | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Brass, etc. |
| Gaskets | Graphite, PTFE, Rubber, etc. |
