Fugitive Emission Valves
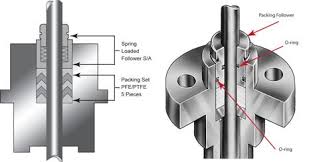
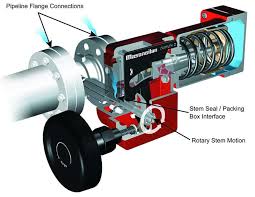
The Application of Fugitive Emission Valves
Introducing Fugitive Emission Valves, including ball valve fugitive emissions testing and compliance with fugitive emission test standards for valves. As a leader in valve technology, Cameron offers solutions addressing environmental concerns. Fugitive emissions, often from valve leaks, pose environmental and safety risks. Cameron‘s valves undergo rigorous fugitive emission tests to meet industry standards like ISO 15848 and API 622. These tests ensure minimal emissions, enhancing environmental protection and operator safety. With Cameron‘s Fugitive Emission Valves, industries can mitigate emissions effectively, meeting regulatory requirements while promoting sustainability.
What Are The Types Of Fugitive Emission Valves?
- Fugitive Emission Ball Valves: These valves feature a ball mechanism for controlling flow and are designed to minimize fugitive emissions through proper sealing and testing.
- Fugitive Emission Gate Valves: Gate valves are used to stop or start the flow of fluid and are equipped with sealing mechanisms to reduce fugitive emissions.
- Fugitive Emission Globe Valves: Globe valves regulate flow by moving a plug or disc against the flow path, and special designs are available to minimize fugitive emissions.
- Fugitive Emission Butterfly Valves: Butterfly valves control flow using a disc-shaped closure element, and certain models are designed to meet fugitive emission standards.
- Fugitive Emission Control Valves: These valves are specifically designed to regulate the flow of fluids while meeting stringent fugitive emission requirements.
- Fugitive Emission Relief Valves: Relief valves are used to protect equipment or systems from overpressure situations and can be designed to minimize fugitive emissions.
What Is Fugitive Emission Valves?
Fugitive emission valves are specialized valves designed to minimize the escape of gases or liquids into the environment. These valves are crucial in industries where even small leaks can pose environmental and safety risks. They feature robust sealing mechanisms and undergo rigorous testing to ensure compliance with emission standards, such as ISO 15848 and API 622. Fugitive emission valves play a vital role in promoting environmental sustainability and maintaining safe operating conditions in industrial facilities.
How Does Fugitive Emission Valves?
Fugitive emission valves operate by utilizing advanced sealing mechanisms to minimize the escape of gases or liquids. These valves are designed with tight tolerances and durable materials to prevent leaks. During operation, the valve’s sealing components create a secure barrier, effectively containing the fluid or gas within the system. Through regular maintenance and adherence to strict testing standards, fugitive emission valves ensure minimal emissions, contributing to environmental protection and safety compliance in industrial settings.
Features of Fugitive Emission Valves
- Advanced Sealing Mechanisms: Fugitive emission valves feature sophisticated sealing mechanisms such as bellows seals or packing glands to ensure tight closure and minimize emissions.
- Compliance with Standards: These valves are designed and tested to meet stringent industry standards like ISO 15848 and API 622, ensuring reliability and environmental compliance.
- Rugged Construction: Built from high-quality materials such as stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloys, fugitive emission valves offer durability and longevity in harsh industrial environments.
- Leak Prevention: With precision engineering and tight tolerances, these valves effectively prevent leaks, reducing the risk of environmental contamination and ensuring operator safety.
- Testing and Certification: Prior to installation, fugitive emission valves undergo thorough testing to verify their performance and compliance with emissions standards, providing peace of mind to users.
- Customization Options: Manufacturers offer customization options to tailor valves to specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and emission control in diverse industrial settings.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fugitive Emission Valves
Advantages:
- Environmental Protection: Fugitive emission valves significantly reduce the release of harmful substances into the environment, contributing to environmental protection and sustainability.
- Regulatory Compliance: These valves help industries comply with stringent environmental regulations and standards, avoiding fines and penalties associated with emissions violations.
- Safety: By minimizing leaks, fugitive emission valves enhance workplace safety by reducing the risk of exposure to hazardous substances for workers and nearby communities.
- Cost Savings: While initial investment costs may be higher, fugitive emission valves can lead to long-term cost savings through reduced emissions, lower maintenance costs, and fewer regulatory compliance issues.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Initial Cost: Fugitive emission valves often come with a higher initial purchase price compared to conventional valves, which may deter some buyers.
- Complexity: The design and installation of fugitive emission valves can be more complex, requiring specialized knowledge and skills, which may increase installation and maintenance costs.
- Maintenance Requirements: These valves may require more frequent maintenance and inspection to ensure proper functioning and compliance with emission standards, leading to increased maintenance costs and downtime.
The Specifications of Fugitive Emission Valves
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Fugitive Emission Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, PVC, etc. |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, Grooved, etc. |
| Thread Standard | ANSI B1.20.1, BSPT, NPT, etc. |
| Thread Size | 1/2 inch, 3/4 inch, 1 inch, etc. |
| Body Material | Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, PVC, etc. |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Oil, Gas, Steam, Chemicals, etc. |
| Handle Type | Handwheel, Lever, Gear Operator, Electric Actuator, Pneumatic Actuator, etc. |
| Handle Material | Steel, Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Plastic, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | 150 psi, 300 psi, 600 psi, etc. |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | 10.3 bar, 20.7 bar, 41.4 bar, etc. |
| Operating Pressure | 0-100 psi, 0-200 psi, 0-400 psi, etc. |
The Installation Steps for Fugitive Emission Valves
- Preparation: Gather all necessary tools and equipment, including wrenches, bolts, nuts, and gaskets required for the installation.
- Location Selection: Choose a suitable location for installing the valve, ensuring easy access for maintenance and operation.
- Valve Inspection: Thoroughly inspect the fugitive emission valve, checking for any damage, defects, or debris that could affect its performance.
- Seal Inspection: Verify the condition of the sealing components, such as gaskets or packing glands, ensuring they are clean and in good condition.
- Alignment: Ensure proper alignment of the valve with the piping system, using alignment marks or indicators if necessary.
- Attachment: Securely attach the valve to the piping system using appropriate fasteners, such as bolts or screws, following the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Tightening: Gradually tighten the fasteners in a crisscross pattern to evenly distribute the load and ensure a secure fit without damaging the valve or the piping.
- Sealing Verification: Conduct a leakage test to verify the integrity of the valve’s seals and connections, ensuring there are no leaks before putting the valve into service.
- Pressure Testing: Perform a pressure test to verify the valve’s performance under operating conditions, ensuring it can withstand the maximum working pressure without leaking or failing.
- Documentation: Record the installation details, including torque values, pressure test results, and any other relevant information for future reference and maintenance.
The Operation Theory of Fugitive Emission Valves
- Sealing Mechanisms: Fugitive emission valves employ advanced sealing mechanisms, such as bellows seals or packing glands, to create a tight seal between the valve components. This prevents the escape of fluids or gases and minimizes fugitive emissions.
- Leakage Prevention: Specialized designs and materials are used to prevent leakage at various points within the valve, including the stem, seat, and body. This helps maintain the integrity of the sealing system and reduces the risk of fugitive emissions.
- Testing and Certification: Low fugitive emission valves undergo rigorous testing to verify their performance and compliance with fugitive emissions standards for valves. This includes testing for leakage rates under different operating conditions to ensure minimal emissions.
- Material Selection: High-quality materials are selected for construction, such as corrosion-resistant alloys or polymers, to enhance durability and minimize the potential for leaks or emissions.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: Regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of low fugitive emission valves. This includes periodic inspections, seal replacements, and performance testing to detect and address any potential issues promptly.
The Parameters Chart of Fugitive Emission Valves
| Parameter | Material Options |
|---|---|
| Valve Type | Ball, Gate, Globe, Butterfly, Plug, Control, Relief, etc. |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, Brass, Bronze, PVC, etc. |
| Seat Material | PTFE, Graphite, Metal, Soft Seated, Fire-Safe, etc. |
| Stem Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, Inconel, etc. |
| Seal Material | PTFE, Graphite, Viton, Nitrile, EPDM, etc. |
| Packing Material | PTFE, Graphite, Carbon, Aramid, GFO, etc. |
| Bolting Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, Brass, etc. |