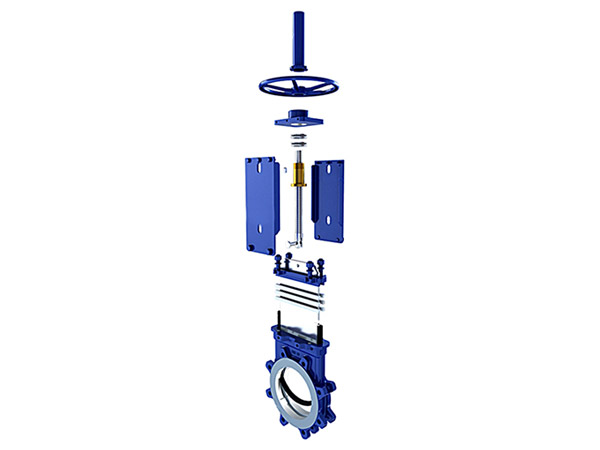
ASME Jacket Safety Valve – 5215 Series
The Application of Jacket Safety Valve
Cameron, a renowned brand in industrial solutions, excels as a safety valve manufacturer offering top-notch valve design solutions for various applications, including the pressure release device known as the Jacket Safety Valve. Engineered for reliability and efficiency, Cameron’s Jacket Safety Valve provides essential overpressure protection in systems handling fluids in jackets or vessels. With innovative design features and precise functionality, Cameron’s safety valves ensure the safety and integrity of equipment and processes, making them indispensable in industries such as oil and gas, chemical, and manufacturing.
What Are The Types Of Jacket Safety Valve?
- Spring-Loaded Jacket Safety Valve: These valves utilize a spring mechanism to maintain a set pressure level. When the pressure in the jacket exceeds the set limit, the spring compresses, allowing the valve to open and release excess pressure.
- Pilot-Operated Jacket Safety Valve: Pilot-operated valves use a smaller control valve (pilot) to sense pressure in the jacket. When the pressure exceeds the set limit, the pilot valve opens, causing the main valve to open and relieve pressure.
- Rupture Disc Jacket Safety Valve: Also known as bursting disc valves, these devices consist of a thin metal disc designed to rupture at a predetermined pressure. When the pressure in the jacket exceeds the disc’s burst pressure, it ruptures, allowing pressure relief.
- Conventional Jacket Safety Valve: These valves operate based on the direct force of the pressure in the jacket. When the pressure exceeds the set limit, the valve’s disc lifts off its seat, allowing excess pressure to escape.
- Balanced Jacket Safety Valve: Balanced valves use additional components, such as bellows or pistons, to balance the pressure across the valve. This design helps maintain consistent valve opening characteristics regardless of inlet pressure variations.
- High-Lift Jacket Safety Valve: High-lift valves feature an extended valve lift, allowing them to discharge larger volumes of fluid at lower pressure differentials. They are commonly used in applications with low backpressure.
What Is Jacket Safety Valve?
A jacket safety valve is a specialized pressure relief device used in systems where fluids are heated or cooled within a jacketed vessel. It provides essential overpressure protection by automatically releasing excess pressure when it exceeds safe limits, preventing potential damage or failure. Jacket safety valves are crucial in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food production, ensuring the safety and integrity of both the equipment and the process.
How to Select the Right Jacket Safety Valve?
When selecting the right jacket safety valve, consider factors such as the operating pressure and temperature, the type of fluid being processed, and the specific safety standards and certifications required. Ensure compatibility with the system’s materials and choose a valve with a suitable pressure rating and response time to effectively protect the equipment and maintain safety.
Features of Jacket Safety Valve
- Pressure Relief:
- Automatic Operation: Opens automatically when pressure exceeds a preset limit, ensuring safe pressure levels within the jacketed vessel.
- Material Compatibility:
- Durable Construction: Made from materials like stainless steel to resist corrosion and handle various fluids, including aggressive chemicals.
- Temperature Resistance:
- High and Low Temps: Designed to operate effectively in a wide range of temperatures, accommodating both heating and cooling processes.
- Adjustability:
- Set Pressure: Can be adjusted to meet specific system pressure requirements, providing flexibility and precision.
- Leak Prevention:
- Sealing Mechanism: Equipped with reliable seals to prevent leaks when not in operation, maintaining system integrity.
- Compliance:
- Industry Standards: Meets or exceeds relevant safety and quality standards, ensuring reliable performance and regulatory compliance.
- Versatility:
- Multiple Applications: Suitable for various industries, including chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food production.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Jacket Safety Valve
Advantages:
- Pressure Protection:
- Overpressure Prevention: Automatically relieves excess pressure, protecting equipment and ensuring safe operation.
- Durability:
- Robust Construction: Made from high-quality materials like stainless steel, ensuring long-lasting performance even in harsh environments.
- Temperature Handling:
- Wide Range: Effective in both high and low-temperature applications, suitable for various industrial processes.
- Adjustability:
- Customizable Settings: Adjustable set pressure allows for tailored protection specific to system requirements.
- Compliance:
- Standards Adherence: Meets industry standards and certifications, ensuring reliability and regulatory compliance.
- Versatility:
- Multiple Uses: Applicable in various industries, such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food production.
Disadvantages:
- Maintenance Requirements:
- Regular Upkeep: Requires periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Initial Cost:
- Expense: High-quality jacket safety valves can be expensive to purchase and install.
- Complexity:
- Installation and Adjustment: Proper installation and adjustment may require specialized knowledge and skills.
- Potential for Leakage:
- Seal Integrity: Although designed to prevent leaks, seals can wear over time and may require replacement to maintain effectiveness.
- Size and Space:
- Installation Space: May require sufficient space for installation, which can be a constraint in compact systems.

The Specifications of Jacket Safety Valve
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Jacket Safety Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel (316) |
| Attachment Type | Flanged or Threaded |
| Thread Standard | ANSI B1.20.1 (NPT) |
| Thread Size | 1/2 inch to 2 inches |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel (304 or 316) |
| Safe for Use With | Steam, Water, Chemicals |
| Handle Type | Lever or Wheel |
| Handle Material | Stainless Steel or Aluminum |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | 600 psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | 41.37 bar |
| Operating Pressure | 10 psi to 300 psi |
The Installation Steps for Jacket Safety Valve
- Prepare Tools and Materials
- Ensure all necessary tools and equipment are ready, including wrenches, bolts, nuts, sealing gaskets, and lubricating oil.
- Check that the Jacket Safety Valve and its components are intact and undamaged.
- Inspect Pipes and Interfaces
- Ensure the pipeline system is completely shut down and depressurized.
- Clean the pipe interfaces to remove any debris and dirt to ensure a good seal.
- Install the Sealing Gasket
- Place a properly sized sealing gasket at the pipe interface, ensuring it is flat and not deformed.
- Connect the Jacket Safety Valve
- Align the Jacket Safety Valve with the pipe interface, ensuring the correct direction of the valve’s inlet and outlet.
- Hand-tighten the bolts to secure the valve in place, ensuring it is correctly positioned.
- Secure Bolts and Nuts
- Using a wrench, tighten the bolts and nuts in a diagonal sequence to ensure even pressure on the valve.
- Check the tightening torque of the bolts to ensure it meets the manufacturer’s recommended standards, generally 20-30 Nm (Newton meters).
- Check for Leaks
- After installation, gradually introduce a small amount of pressure into the system and check the valve and pipe interface for leaks.
- If any leaks are detected, readjust the gasket position and retighten the bolts.
- Connect Control Lines
- Depending on the valve model, connect the control lines (such as pneumatic or hydraulic control systems) to the Jacket Safety Valve.
- Ensure the control lines are securely connected and leak-free.
- Lubrication and Maintenance
- After installation, apply an appropriate amount of lubricating oil to the moving parts of the valve to reduce friction and wear.
- Regularly inspect and maintain the Jacket Safety Valve to ensure long-term stable operation.
- Testing and Commissioning
- After installation, perform system tests to confirm the Jacket Safety Valve opens and closes properly.
- Adjust as needed to ensure the valve releases pressure correctly at the set pressure.
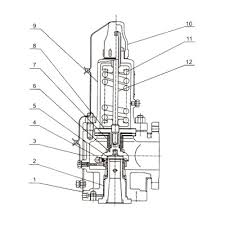
The Operation Theory of Jacket Safety Valve
- Pressure Detection and Response:
- The valve is equipped with a sensing mechanism that detects the pressure within the system.
- When the system pressure exceeds a predetermined set point, the valve activates to release the excess pressure.
- Spring-Loaded Mechanism:
- Most Jacket Safety Valves use a spring-loaded mechanism. The spring is calibrated to a specific pressure.
- When the system pressure pushes against the valve disc with a force greater than the spring force, the valve opens.
- Pressure Release:
- Upon opening, the valve allows the pressurized
The Operation Theory of Jacket Safety Valve
A Jacket Safety Valve is designed to protect pressure vessels and systems from overpressure conditions. Here’s a detailed look at its operation theory:
- Pressure Detection and Response:
- The valve is equipped with a sensing mechanism that detects the pressure within the system.
- When the system pressure exceeds a predetermined set point, the valve activates to release the excess pressure.
- Spring-Loaded Mechanism:
- Most Jacket Safety Valves use a spring-loaded mechanism. The spring is calibrated to a specific pressure.
- When the system pressure pushes against the valve disc with a force greater than the spring force, the valve opens.
- Pressure Release:
- Upon opening, the valve allows the pressurized fluid (liquid or gas) to escape, reducing the system pressure.
- The release continues until the system pressure drops back to safe levels, allowing the spring to close the valve.
- Seal and Reseal:
- Once the excess pressure is released and the system pressure returns to a safe level, the spring force pushes the valve disc back into place, sealing the valve.
- The valve remains closed until another overpressure event occurs.
Valve Installation Guide
Here is a general installation guide for valves, including the Jacket Safety Valve:
- Preparation:
- Gather all necessary tools and materials such as wrenches, bolts, nuts, gaskets, and lubricants.
- Inspect the valve and all components to ensure they are in good condition.
- Pipeline Inspection:
- Ensure the pipeline is depressurized and clean.
- Remove any debris from the pipeline interface to ensure a proper seal.
- Gasket Placement:
- Place an appropriately sized gasket on the pipeline interface.
- Ensure the gasket is flat and not deformed.
- Valve Alignment and Connection:
- Align the valve with the pipeline interface, ensuring correct orientation.
- Hand-tighten the bolts to hold the valve in place.
- Bolt Tightening:
- Use a wrench to tighten the bolts in a crisscross pattern for even pressure distribution.
- Check and confirm the torque of the bolts meets the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Leak Testing:
- Gradually introduce pressure to the system and check for leaks at the valve connections.
- If leaks are found, adjust and retighten the bolts as necessary.
- Control Line Connection:
- For valves with control lines, connect these to the appropriate ports.
- Ensure connections are secure and leak-free.
- Lubrication and Maintenance:
- Apply lubricants to moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
- Perform regular maintenance checks to ensure ongoing proper function.
- System Testing:
- Conduct a full system test to verify the valve operates correctly.
- Make any necessary adjustments to ensure reliable performance.
Water Heater Safety Valve
The Water Heater Safety Valve (also known as the Temperature and Pressure Relief Valve) is crucial for protecting water heaters from excessive pressure and temperature. Here’s an overview of its function and installation:
- Operation Theory:
- Temperature Sensitivity:
- The valve is designed to open when the water temperature exceeds a safe level, typically around 210°F (99°C).
- Pressure Sensitivity:
- The valve also opens if the pressure within the tank exceeds safe levels, usually set around 150 psi (10.3 bar).
- Release Mechanism:
- When either threshold is breached, the valve opens to release hot water and steam, reducing the pressure and temperature.
- Temperature Sensitivity:
- Installation Steps:
- Preparation:
- Ensure the water heater is off and the system is depressurized.
- Gather tools including pipe wrenches, Teflon tape, and the new safety valve.
- Removing the Old Valve:
- Drain the water heater to below the level of the safety valve.
- Use a pipe wrench to remove the old valve.
- Installing the New Valve:
- Apply Teflon tape to the threads of the new valve.
- Screw the new valve into place, ensuring a snug fit.
- Testing:
- Refill the water heater and restore power.
- Check the new valve for leaks and proper operation by lifting the test lever.
- Ensure the discharge pipe directs water safely away from the heater.
- Preparation: