DBB Monoflange Ball Valve
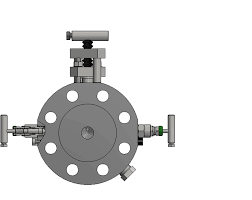
The Application of DBB Monoflange Ball Valve
The DBB Monoflange Ball Valve is a compact and versatile valve designed for reliable isolation and venting in various industrial applications. Unlike lug vs wafer butterfly valves, the DBB Monoflange Ball Valve features a single-body design with integrated flanges, reducing potential leak points and installation complexity. This design makes it ideal for applications where space is limited or weight considerations are crucial. With its double block and bleed (DBB) functionality, the valve allows for isolation of the process fluid from both upstream and downstream connections, simplifying maintenance and ensuring safety. The Monoflange Ball Valve offers superior performance, reliability, and ease of installation, making it a preferred choice in critical process control systems.
The Parameter of DBB Monoflange Ball Valve
- Valve Type: DBB Monoflange Ball Valve
- Brand: Manufactured by Cameron
- Design: Single-body design with integrated flanges
- Functionality: Double block and bleed (DBB) functionality
- Size Range: Available in various sizes, including 6″ and 8″
- Material: Constructed from high-quality materials for durability
- End Connection: Equipped with integrated flanges for easy installation
- Sealing Mechanism: Utilizes advanced sealing technology for leak-proof performance
- Application: Suitable for critical process control applications in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, and power generation
- Versatility: Offers reliability, efficiency, and safety in fluid control systems
Feathures:
- Flanged inlet connections conforming to ASME B16.5 standards, available in sizes ranging from 1/2” to 2”.
- Standard 1/2” NPT female outlet connection.
- Standard 1/2” NPT female bleed port equipped with a Hex Plug.
- Standard Outside Screw and Yoke (OS&Y) design with graphite packing, with optional PTFE packing available.
- Standard needle valve featuring PTFE packing, with the option to choose graphite packing.
The Operation Theory of DBB Monoflange Ball Valve
The operation theory of the DBB Monoflange Ball Valve is based on the principle of a float ball valve. Similar to the symbol for ball valve, it utilizes a ball with a hole through its center to control the flow of fluid. When the valve is open, the ball rotates to align the hole with the flow path, allowing fluid to pass through. Conversely, when closed, the ball rotates perpendicular to the flow path, blocking fluid flow. This simple yet effective mechanism provides reliable isolation and venting in critical process control applications, including ball valve plumbing systems.

The Parameters Table of DBB Monoflange Ball Valve
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Valve Type | DBB Monoflange Ball Valve |
| Brand | Cameron |
| Design | Single-body with integrated flanges |
| Functionality | Double block and bleed (DBB) |
| Size Range | Various sizes available, including 6″ and 8″ |
| Material | High-quality materials for durability |
| End Connection | Integrated flanges for easy installation |
| Sealing Mechanism | Advanced sealing technology for leak-proof performance |
| Application | Suitable for critical process control applications |
| Versatility | Provides reliability, efficiency, and safety |
Relevant Information about DBB Monoflange Ball Valve
- Rotor (Rator): The rotor in a valve typically refers to the rotating part of a control valve, such as a ball or disc, which regulates the flow of fluid through the valve. In the case of the DBB Monoflange Ball Valve, the ball serves as the rotor.
- Stator: The stator is not typically a component of a valve. It’s commonly found in motors or generators and serves to provide a stationary magnetic field.
- Universal Joint: Universal joints are not typically found in valves. They are commonly used in mechanical systems to transmit torque between non-aligned shafts.
- Shaft Seal: Shaft seals may be present in valves to prevent leakage along the valve stem. These seals can be made of materials like elastomers or PTFE.
- Driving System: In manual valves like the DBB Monoflange Ball Valve, the driving system involves a handle or lever that the operator uses to manually open or close the valve. In automated valves, a driving system such as an electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuator is used to control the valve remotely.
