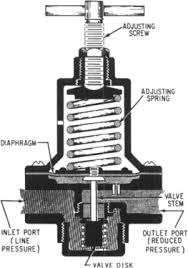
Pressure Regulating Valve
The Application of Power Plant Drain Control Valves
Introducing Cameron’s expertise in fluid control solutions, our Power Plant Drain Control Valves play a pivotal role in managing drainage systems. These valves, including air pressure regulator valve, gas pressure regulator valve, and air pressure regulating valve, ensure efficient discharge of water, steam, and other fluids in power plants. Designed for reliability and precision, they contribute to optimal plant performance and safety. Cameron’s commitment to quality ensures that our drain control valves meet the rigorous demands of power generation, providing seamless operation and environmental compliance.
What Are The Types Of Power Plant Drain Control Valves?
- Gate Valves: These valves provide a tight shut-off and are commonly used for larger diameter drain lines in power plants.
- Ball Valves: Known for their quick operation and simple design, ball valves are suitable for applications requiring frequent operation and tight shut-off.
- Butterfly Valves: Ideal for large flow applications, butterfly valves offer excellent control and can handle high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.
- Globe Valves: Globe valves provide precise control of flow rate and are often used in systems requiring throttling or modulation.
- Diaphragm Valves: These valves offer excellent sealing properties and are suitable for handling corrosive fluids or slurries in power plant drain systems.
What Is Power Plant Drain Control Valves?
Power Plant Drain Control Valves are essential components in power generation facilities, designed to regulate the discharge of water, steam, or other fluids from various systems within the plant. These valves ensure efficient drainage while maintaining operational safety and integrity. They come in various types, including gate valves, ball valves, and butterfly valves, each tailored to specific applications and operating conditions. By facilitating effective fluid management, Power Plant Drain Control Valves contribute to the overall reliability and performance of power plants, enhancing their efficiency and minimizing downtime.
How to Select the Right Power Plant Drain Control Valves?
Selecting the appropriate Power Plant Drain Control Valves involves considering factors such as flow rate, pressure, temperature, fluid characteristics, and system requirements. Assessing the specific application needs and consulting with experts can help in choosing the right valve type, size, material, and features to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and safety in power plant drainage systems. Additionally, evaluating the valve’s compatibility with existing infrastructure and maintenance requirements is crucial for long-term efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Features of Power Plant Drain Control Valves
- Identify Application Requirements:
- Determine the specific needs of the power plant drainage system, including flow rate, pressure, temperature, and fluid characteristics.
- Valve Type:
- Choose the appropriate valve type based on the application, such as gate valves for larger diameter lines or ball valves for quick operation.
- Material Selection:
- Consider the compatibility of valve materials with the fluid being handled, ensuring resistance to corrosion, erosion, and high temperatures.
- Size and Configuration:
- Select the valve size and configuration that best matches the pipe dimensions and flow requirements of the system.
- Operating Conditions:
- Evaluate the operating conditions, including pressure fluctuations and temperature variations, to ensure the selected valves can withstand the environment.
- Control Mechanism:
- Determine the desired control mechanism, whether manual, pneumatic, or electric, based on the level of automation and control required.
- Reliability and Maintenance:
- Assess the reliability and maintenance requirements of the valves, considering factors such as durability, ease of maintenance, and availability of spare parts.
- Compliance and Standards:
- Ensure that the selected valves comply with industry standards and regulations for safety, performance, and environmental protection.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Power Plant Drain Control Valves
Advantages:
Efficient Fluid Management:
- Drain control valves ensure efficient drainage, maintaining optimal fluid levels and preventing system overflows. Enhanced Safety:
- Proper drainage management reduces the risk of equipment damage, accidents, and environmental hazards within power plants. Improved System Reliability:
- These valves contribute to the overall reliability and longevity of power plant systems by regulating fluid flow and preventing blockages. Customized Solutions:
- Various types and configurations of drain control valves are available, allowing for tailored solutions to meet specific plant requirements. Reduced Downtime:
- Reliable operation and minimal maintenance requirements of these valves help minimize downtime and ensure uninterrupted power generation. Disadvantages:
Initial Cost:
- High-quality drain control valves may have an initial upfront cost, although they often provide long-term cost savings through improved efficiency and reduced maintenance. Complexity:
- Selecting and installing the right valves for specific applications may require expertise and careful consideration of various factors, adding complexity to the process. Potential for Failure:
- Like any mechanical component, drain control valves can experience wear and tear over time, leading to potential failures if not properly maintained. Environmental Impact:
- Improperly functioning or malfunctioning drain control valves can lead to environmental pollution or damage if they fail to contain fluids within the plant premises. Compatibility Issues:
- Ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure and systems may pose challenges when selecting and installing drain control valves in power plants.

The Specifications of Power Plant Drain Control Valves
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Ball Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel |
| Attachment Type | Flanged |
| Thread Standard | N/A |
| Thread Size | N/A |
| Body Material | Carbon Steel |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Oil, Gas |
| Handle Type | Lever |
| Handle Material | Stainless Steel |
| Maximum Working Pressure | 600 psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure | 41.37 bar |
| Operating Pressure | 0 to 150 psi |
The Installation Steps for Power Plant Drain Control Valves
- Preparation:
- Gather all necessary tools and equipment.
- Review manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines.
- Shut down relevant power plant systems and isolate drain lines.
- Valve Inspection:
- Inspect the valve for any visible damage or defects.
- Ensure that the valve specifications match the installation requirements.
- Pipe Preparation:
- Clean the pipe ends thoroughly to remove dirt, debris, or contaminants.
- Ensure that the pipe ends are smooth and free from burrs or irregularities.
- Valve Positioning:
- Position the valve at the desired location along the drain line.
- Ensure proper alignment with the pipe and adjacent components.
- Attachment:
- Use appropriate fittings and connectors to secure the valve to the pipe.
- Tighten all connections securely using the recommended torque values.
- Sealing:
- Apply sealant or thread tape to the threaded connections to ensure a leak-free seal.
- Inspect for any signs of leakage and make adjustments as necessary.
- Testing:
- Conduct a pressure test to verify the integrity of the installation.
- Gradually increase the pressure to the operating level and check for leaks.
- Final Checks:
- Confirm that the valve operates smoothly and opens/closes correctly.
- Ensure proper labeling and identification of the valve for future maintenance.
- System Re-Activation:
- Once the installation is complete and verified, re-activate power plant systems and monitor for abnormalities.
The Operation Theory of Power Plant Drain Control Valves
- Power Plant Drain Control Valves:
- These valves regulate the discharge of water, steam, or other fluids from various systems within a power plant. They ensure efficient drainage while maintaining operational safety and integrity. Typically, they operate in response to signals from the control system, opening or closing to manage fluid levels and pressure within the plant.
- Fuel Pressure Regulator Valves:
- Fuel pressure regulator valves maintain consistent fuel pressure within the fuel system. They regulate the flow of fuel to the engine or combustion system, ensuring optimal fuel atomization and combustion efficiency. By adjusting the pressure based on engine demand or operating conditions, these valves help maximize engine performance while minimizing fuel consumption and emissions.
- Oil Pressure Regulator Valves:
- Oil pressure regulator valves maintain the desired oil pressure within the lubrication system of engines or machinery. They ensure proper lubrication of moving parts by controlling the flow of oil through the system. These valves respond to changes in oil pressure, adjusting the flow rate to maintain optimal operating conditions and prevent damage due to insufficient or excessive oil pressure.
The Parameters Chart of Power Plant Drain Control Valves
| Parameter | Material |
|---|---|
| Valve Type | Gate Valve, Ball Valve, Butterfly Valve, etc. |
| Valve Body Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Brass, etc. |
| Valve Seat Material | PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), EPDM, Viton, etc. |
| Valve Trim Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, Bronze, etc. |
| Stem Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, etc. |
| Bonnet Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Brass, etc. |
| Seat Ring Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, etc. |
| Disc Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Bronze, etc. |
| Actuator Material | Aluminum Alloy, Ductile Iron, Cast Iron, etc. |
| Gasket Material | Graphite, PTFE, Nitrile, etc. |
| Packing Material | PTFE, Graphite, Kevlar, etc. |

