Full port ball valve VS reduced port ball valve
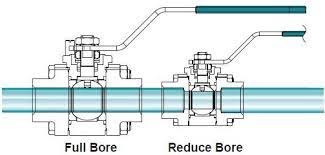
The Application of Full port ball valve VS reduced port ball valve
Cameron, a renowned name in the valve industry, offers both full port ball valve and reduced port ball valve options to cater to diverse application requirements. The choice between a full port ball valve and a reduced port ball valve depends on the specific needs of the application. Full port ball valves provide a straight-through flow path with minimal resistance, making them ideal for high-flow and low-pressure drop applications. Conversely, reduced port ball valves feature a smaller opening, resulting in a higher pressure drop, but they offer enhanced control and better suitability for applications with tighter space constraints. Understanding the nuances between full port vs reduced port ball valve performance is crucial in selecting the appropriate valve solution for your specific needs.
What Are The Types Of Full port ball valve VS reduced port ball valve?
Types of Full Port Ball Valve:
- Standard Full Port Ball Valve: Provides a straight-through flow path with minimal obstruction, allowing for maximum flow capacity.
- Trunnion-Mounted Full Port Ball Valve: Features a trunnion-mounted ball design for increased stability and reliability in high-pressure applications.
- Floating Full Port Ball Valve: The ball is supported by the line pressure, allowing for a more compact design and lower-cost construction.
Types of Reduced Port Ball Valve:
- Standard Reduced Port Ball Valve: Has a smaller orifice diameter compared to the pipe size, resulting in a higher pressure drop but better control.
- Segmented Reduced Port Ball Valve: Utilizes a segmented ball design to optimize flow characteristics and reduce pressure loss.
- Characterized Reduced Port Ball Valve: Incorporates a specially designed ball profile to provide a more linear flow characteristic and improved control.
What Is Full port ball valve VS reduced port ball valve?
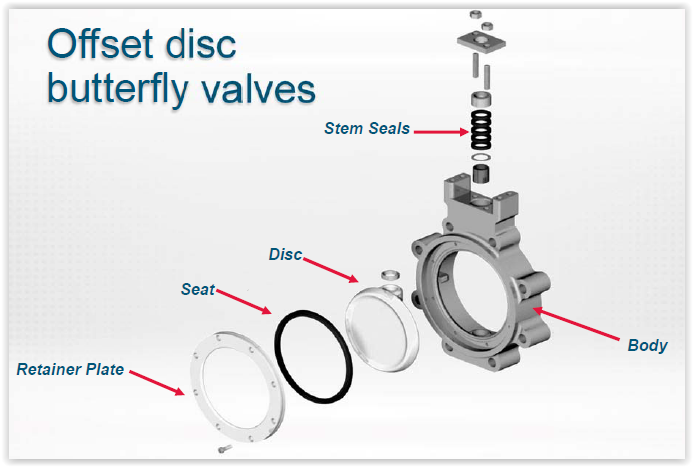
Full port ball valves and reduced port ball valves are two distinct types of ball valve designs that offer different flow characteristics and performance capabilities. A full port ball valve features a bore size that is equal to the pipe diameter, allowing for a straight-through, unobstructed flow path and minimal pressure drop. In contrast, a reduced port ball valve has a smaller bore size compared to the pipe diameter, resulting in a higher pressure drop but providing better flow control and suitability for applications with space constraints. The choice between full port and reduced port ball valves depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as flow rate, pressure, and control needs. Cameron, a leading valve manufacturer, offers a wide range of both full port and reduced port ball valve options to cater to diverse industrial requirements.
How to Select the Right Full port ball valve VS reduced port ball valve?
Flow Requirements:
- Full port ball valves are ideal for applications requiring high flow rates and minimal pressure drop.
- Reduced port ball valves are better suited for applications where flow control and precise throttling are necessary.
Pressure Drop:
- Full port ball valves have a lower pressure drop due to their straight-through flow path.
- Reduced port ball valves have a higher pressure drop, but can provide better control over the flow.
Space Constraints:
- Reduced port ball valves often have a smaller footprint, making them suitable for installations with limited space.
- Full port ball valves may require more clearance due to their larger size.
Fluid Characteristics:
- Full port ball valves are generally more suitable for clean, unobstructed fluids.
- Reduced port ball valves can handle fluids with higher levels of solids or viscosity.
Features of Full port ball valve VS reduced port ball valve
Flow Capacity:
- Full Port Ball Valve: Provides maximum flow capacity due to the straight-through, unobstructed flow path.
- Reduced Port Ball Valve: Has a smaller orifice, resulting in a higher pressure drop but better flow control.
Pressure Drop:
- Full Port Ball Valve: Experiences lower pressure drop, making it suitable for high-flow, low-pressure applications.
- Reduced Port Ball Valve: Exhibits a higher pressure drop, but offers enhanced control over the flow.
Space Requirement:
- Full Port Ball Valve: Generally requires more installation space due to its larger size.
- Reduced Port Ball Valve: Has a smaller footprint, making it more suitable for installations with limited space.
Fluid Handling:
- Full Port Ball Valve: Better suited for clean, unobstructed fluids.
- Reduced Port Ball Valve: Can handle fluids with higher levels of solids or viscosity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Full port ball valve VS reduced port ball valve
Advantages of Full Port Ball Valve:
- Higher flow capacity and lower pressure drop
- Straight-through flow path for unobstructed fluid passage
- Suitable for high-flow, low-pressure applications
Disadvantages of Full Port Ball Valve:
- Larger physical size and footprint
- Less control over flow rate and pressure
Advantages of Reduced Port Ball Valve:
- Better flow control and throttling capabilities
- Smaller physical size and footprint
- Suitable for handling fluids with solids or higher viscosity
Disadvantages of Reduced Port Ball Valve:
- Higher pressure drop due to the reduced orifice size
- Lower overall flow capacity compared to full port designs

The Specifications of Full port ball valve VS reduced port ball valve
| Specification | Full Port Ball Valve | Reduced Port Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Standard Full Port Ball Valve | Segmented Reduced Port Ball Valve |
| Ball Material | 316 Stainless Steel | 304 Stainless Steel |
| Attachment Type | Flanged | Threaded |
| Thread Standard | ANSI B16.5 | NPT |
| Thread Size | 2 inch | 1.5 inch |
| Body Material | Carbon Steel | Brass |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Oil, Gas | Corrosive Fluids |
| Handle Type | Lever | Gear Operated |
| Handle Material | Aluminum | Cast Iron |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | 1000 | 600 |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | 69 | 41.4 |
| Operating Pressure (psi) | 800 | 500 |
| Operating Pressure (bar) | 55.2 | 34.5 |
The Installation Steps for Full port ball valve VS reduced port ball valve
Installation Steps for Full Port Ball Valve:
- Ensure the pipeline is properly aligned and supported to prevent unnecessary stress on the valve.
- Clean the pipe ends and valve flanges to remove any dirt, debris, or residue.
- Apply a suitable sealant or gasket material between the valve flanges and pipe ends.
- Position the full port ball valve in the desired orientation and secure the flanges using the recommended torque values.
- Connect the valve to the power source (if applicable) and ensure proper wiring for any electronic components.
- Perform a thorough leak test to verify the integrity of the installation.
- Gradually open the valve to the desired position and check for any leaks or abnormal operation.
Installation Steps for Reduced Port Ball Valve:
- Verify the thread size and type (NPT) match the pipe connections.
- Apply a suitable thread sealant to the valve’s threaded ends.
- Carefully thread the reduced port ball valve into the pipe fittings, ensuring proper alignment and avoiding cross-threading.
- Use a wrench to tighten the valve, applying the recommended torque values.
- Connect the valve to the power source (if applicable) and ensure proper wiring for any electronic components.
- Perform a leak test to ensure a tight seal at the threaded connections.
- Slowly open the valve to the desired position and check for any leaks or abnormal operation.
The Operation Theory of Full port ball valve VS reduced port ball valve
Operation Theory of Full Port Ball Valve:
- Flow Path: The full port ball valve features a straight-through, unobstructed flow path, allowing for maximum flow capacity and minimal pressure drop.
- Ball Mechanism: The spherical ball rotates within the valve body, providing a simple on/off operation. When the valve is fully open, the ball is parallel to the flow, creating a clear path for the fluid.
- Flow Control: Full port ball valves are primarily used for on/off control, as they are not well-suited for fine-tuned flow regulation due to the lack of a throttling mechanism.
- Pressure Handling: The full port design can withstand high pressures due to the even distribution of forces on the ball surface.
Operation Theory of Reduced Port Ball Valve:
- Flow Path: The reduced port ball valve features a smaller orifice compared to the full port design, creating a more tortuous flow path.
- Ball Mechanism: Similar to the full port valve, the spherical ball rotates to control the flow, but the reduced port creates a higher pressure drop.
- Flow Control: Reduced port ball valves are better suited for flow throttling and control applications, as the smaller orifice allows for more precise regulation of the fluid flow.
- Pressure Handling: The reduced port design can handle moderate to high pressures, but the pressure drop across the valve is generally higher compared to a full port valve.