Float Check Valve
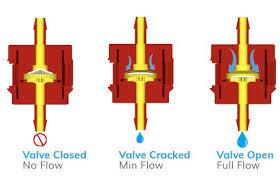
The Application of Float Check Valve
Cameron, a renowned brand in industrial solutions, offers a versatile range of valves, including the float check valve. Also known as a floating ball check valve or one way check valve, this valve is crucial in preventing backflow in piping systems. It operates on the principle of a floating ball that rises to block reverse flow when the forward flow stops. The ball moves freely within the valve body, allowing unimpeded flow in one direction while blocking flow in the opposite direction. Widely used in applications like compressor systems, the float check valve ensures system efficiency and safety by maintaining fluid or gas flow in the desired direction and preventing costly damage from backflow.
What Are The Types Of Float Check Valve?
- Floating Ball Check Valve: This type of valve utilizes a floating ball mechanism to regulate flow, allowing unidirectional flow while preventing backflow when the pressure drops.
- Piston Check Valve: In a piston check valve, a piston moves within the valve body to control flow direction. When the pressure on one side exceeds the other, the piston moves to allow flow, but it closes to prevent backflow when pressure imbalances occur.
- Diaphragm Check Valve: Diaphragm check valves use a flexible diaphragm to regulate flow. When the pressure on one side of the valve exceeds the other, the diaphragm flexes to allow flow, but it prevents backflow by sealing tightly against the valve seat.
- Spring Check Valve: Spring check valves incorporate a spring mechanism to regulate flow. The spring applies force to keep the valve closed, but when the pressure on one side exceeds the other, it compresses to allow flow while preventing backflow when pressure drops.
What Is Float Check Valve?
A Float Check Valve is a type of check valve designed to allow fluid or gas flow in one direction while preventing backflow in the opposite direction. It typically consists of a floating mechanism, such as a ball or piston, that moves freely within the valve body. When fluid or gas flows in the desired direction, the floating mechanism moves aside, allowing passage. However, when the flow stops or reverses, the floating mechanism returns to its original position, blocking the flow path and preventing backflow. Float check valves are commonly used in various industries to ensure system efficiency and prevent damage from reverse flow.
How Does Float Check Valve work?
A Float Check Valve operates by utilizing a floating mechanism, such as a ball or piston, to regulate the flow of fluid or gas. When the pressure on one side of the valve exceeds the other, the floating mechanism moves aside, allowing flow in the desired direction. However, when the flow stops or reverses, the floating mechanism returns to its original position, blocking the flow path and preventing backflow. This mechanism ensures unidirectional flow, maintaining system efficiency and preventing damage from reverse flow.
Features of Float Check Valve
- Unidirectional Flow: Ensures flow in one direction only, preventing backflow and maintaining system integrity.
- Floating Mechanism: Utilizes a floating ball or piston to regulate flow, allowing for smooth operation and reliable performance.
- Automatic Operation: Functions automatically based on changes in fluid or gas pressure, requiring minimal manual intervention.
- Versatility: Available in various sizes, materials, and configurations to suit different applications and operating conditions.
- Low Maintenance: Requires minimal maintenance due to its simple design and reliable operation, reducing downtime and costs.
- Durable Construction: Constructed from high-quality materials, ensuring long-term durability and resistance to corrosion and wear.
- Wide Application: Suitable for a wide range of industries and applications, including water treatment, HVAC systems, and industrial processes.
- Compact Design: Features a compact and space-saving design, making it ideal for installations with limited space.
Advantages of Float Check Valve
- Prevents Backflow: Ensures unidirectional flow, effectively preventing backflow and maintaining system integrity.
- Automatic Operation: Operates automatically based on changes in fluid or gas pressure, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
- Reliable Performance: Offers reliable and consistent performance over extended periods, minimizing the risk of system failure.
- Low Maintenance: Requires minimal maintenance due to its simple design and robust construction, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Versatile Application: Suitable for various industries and applications, providing flexibility in usage scenarios.
- Cost-Effective: Helps optimize operational costs by reducing the risk of damage from backflow and minimizing maintenance requirements.
- Space-Saving Design: Features a compact design, making it suitable for installations with limited space or where space optimization is essential.
- Long-Term Durability: Constructed from high-quality materials, ensuring long-term durability and resistance to corrosion and wear.
The Specifications of Float Check Valve
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Float Check Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, PVC, Cast Iron |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Socket Weld, Butt Weld |
| Thread Standard | NPT, BSP, BSPT, DIN, JIS, API |
| Thread Size | 1/2 inch to 24 inches (for threaded), 2 inches to 48 inches (for flanged) |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Cast Iron, PVC |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Oil, Gas, Chemicals, Steam, Air |
| Handle Type | Lever, Handwheel, Gear Operator, None (for automatic operation) |
| Handle Material | Stainless Steel, Aluminum Alloy, Plastic |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Up to 1500 psi (103.42 bar) |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Up to 2500 psi (172.37 bar) (for high-pressure models) |
| Operating Pressure | Varies based on specific model and application |
The Parameter of Float Check Valve
- Type: The Float Check Valve is a type of check valve designed to allow fluid or gas flow in one direction while preventing backflow.
- Ball Material: Available in various materials such as stainless steel, brass, PVC, and cast iron to suit different applications and fluid compatibility requirements.
- Attachment Type: Can be flanged, threaded, socket weld, or butt weld, providing flexibility in installation options.
- Thread Standard: Available in NPT, BSP, BSPT, DIN, JIS, and API standards to ensure compatibility with different piping systems.
- Thread Size: Ranges from 1/2 inch to 24 inches for threaded connections and 2 inches to 48 inches for flanged connections, accommodating various pipe sizes.
- Body Material: Constructed from materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, cast iron, or PVC, providing durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Safe for Use With: Suitable for a wide range of fluids, including water, oil, gas, chemicals, steam, and air, depending on the material compatibility.
- Handle Type: Can be equipped with a lever, handwheel, gear operator, or none (for automatic operation), providing options for manual or automatic operation.
- Handle Material: Available in materials such as stainless steel, aluminum alloy, or plastic, providing options for different operating environments.
- Maximum Working Pressure: Maximum working pressure can range up to 1500 psi (103.42 bar) for standard models and up to 2500 psi (172.37 bar) for high-pressure models, ensuring compatibility with various pressure requirements.
- Operating Pressure: Operating pressure varies based on the specific model and application requirements, providing flexibility for different operating conditions.
The Operation Theory of Float Check Valve
The operation theory of a Float Check Valve revolves around its mechanism, ensuring unidirectional flow and preventing backflow. When fluid or gas flows in the desired direction, the buoyant element, typically a ball or piston, moves upward, allowing the flow to pass through freely. However, when the flow stops or reverses, the buoyant element descends, sealing against the valve seat, thus preventing backflow. This operation principle is similar to that of a ball check valve or vacuum check valve, where the buoyant element serves as a barrier to reverse flow, ensuring system integrity and efficiency. Whether in low or high-pressure systems, the Float Check Valve’s reliable operation maintains fluid or gas flow in the intended direction, safeguarding equipment and processes.
The Parameters Table of Float Check Valve
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Float Check Valve |
| Buoyant Element Material | Stainless Steel, Brass, PVC, Cast Iron |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Socket Weld, Butt Weld |
| Thread Standard | NPT, BSP, BSPT, DIN, JIS, API |
| Thread Size | 1/2 inch to 24 inches (for threaded), 2 inches to 48 inches (for flanged) |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Cast Iron, PVC |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Oil, Gas, Chemicals, Steam, Air |
| Handle Type | Lever, Handwheel, Gear Operator, None (for automatic operation) |
| Handle Material | Stainless Steel, Aluminum Alloy, Plastic |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Up to 1500 psi (103.42 bar) |
| Maximum Working Pressure | Up to 2500 psi (172.37 bar) (for high-pressure models) |
| Operating Pressure | Varies based on specific model and application |

