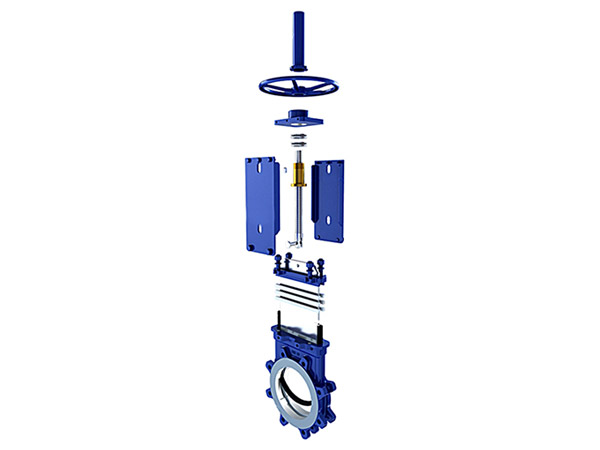
Pressure Seal Valves – Working Principle, vs. Bolted, Gaskets
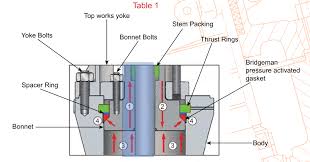
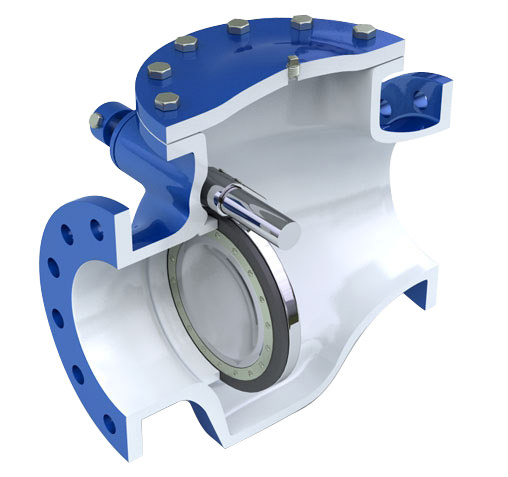
The Application of Pressure Seal Valves
Introducing the robust Cameron Pressure Seal Valves, including the AR220-80 Pressure Seal Gate Valve, AR220-215 Pressure Seal Globe Valves, and AR220-80 Pressure Seal Gate Valves. Engineered for high-pressure applications, these valves feature a unique pressure seal bonnet design, ensuring reliable sealing under extreme conditions. With Cameron’s expertise, these valves offer exceptional performance and durability, making them ideal for critical processes in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, and power generation. The AR220 series exemplifies Cameron’s commitment to innovation and quality, providing peace of mind in demanding environments.
What Are The Types Of Pressure Seal Valves?
- Pressure Seal Gate Valves: These valves feature a gate mechanism that controls the flow of fluid through a sliding or rising stem. They are suitable for high-pressure applications where tight shut-off is required.
- Pressure Seal Globe Valves: Globe valves utilize a disc mechanism to regulate flow by moving perpendicular to the direction of fluid flow. Pressure seal globe valves are designed to provide excellent sealing under high-pressure conditions.
- Pressure Seal Check Valves: Check valves allow flow in one direction while preventing backflow. Pressure seal check valves ensure tight sealing under high-pressure conditions to prevent reverse flow.
- Pressure Seal Ball Valves: Ball valves use a rotating ball with a bore to control flow. Pressure seal ball valves are suitable for high-pressure applications where quick opening and closing are required.
- Pressure Seal Butterfly Valves: Butterfly valves use a disc mounted on a rotating shaft to control flow. Pressure seal butterfly valves are used in high-pressure systems where space is limited and quick operation is needed.
What Is Pressure Seal Valves?
Pressure seal valves are specially designed valves engineered to handle high-pressure applications effectively. Unlike conventional valves, pressure seal valves feature a unique bonnet design that utilizes pressure from the fluid to enhance sealing integrity. This design ensures reliable performance and tight shut-off even under extreme pressure conditions, making pressure seal valves crucial for industries such as oil and gas, power generation, and petrochemicals.
How Does Pressure Seal Valves?
Pressure seal valves operate by utilizing pressure from the fluid to enhance sealing integrity. The unique bonnet design exerts pressure on the sealing surfaces as the internal pressure increases, creating a tighter seal. This mechanism ensures reliable performance and tight shut-off even under extreme pressure conditions, making pressure seal valves ideal for high-pressure applications in various industries.
Features of Pressure Seal Valves
- High Pressure Capability: Pressure seal valves are designed to withstand high-pressure environments, making them suitable for applications where standard valves may fail.
- Enhanced Sealing: The pressure from the fluid enhances the sealing integrity of the valve, ensuring a tight seal even under extreme pressure conditions.
- Reduced Maintenance: Due to their robust construction and superior sealing, pressure seal valves require less frequent maintenance, resulting in reduced downtime and cost savings.
- Wide Range of Sizes: These valves are available in a wide range of sizes to accommodate various piping systems and flow requirements, providing versatility in application.
- Diverse Applications: From oil and gas to power generation and petrochemicals, pressure seal valves find applications in industries where high-pressure sealing is critical.
- Long Service Life: Their durable construction and reliable sealing mechanism contribute to an extended service life, offering long-term performance and reliability.
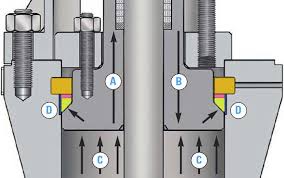
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pressure Seal Valves
Advantages:
- High Pressure Rating: Pressure seal valves are designed to withstand extremely high pressures, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Enhanced Sealing Integrity: The pressure from the fluid helps enhance the sealing integrity of the valve, ensuring tight shut-off even under extreme pressure conditions.
- Reduced Maintenance: Due to their robust construction and superior sealing, pressure seal valves require less frequent maintenance, leading to reduced downtime and cost savings.
- Versatility: These valves are available in a wide range of sizes and configurations, making them suitable for various applications across different industries.
- Long Service Life: Their durable construction and reliable sealing mechanism contribute to an extended service life, providing long-term performance and reliability.
Disadvantages:
- Complex Design: The pressure seal valve design is more complex compared to standard valves, which may result in higher manufacturing costs.
- Higher Initial Cost: Pressure seal valves tend to have a higher initial cost compared to standard valves due to their specialized design and materials.
- Limited Availability: Pressure seal valves may have limited availability compared to standard valves, especially in certain sizes or configurations.
- Potential for Leakage: While pressure seal valves offer excellent sealing integrity, improper installation or maintenance could lead to potential leakage issues.
- Maintenance Challenges: Although pressure seal valves require less frequent maintenance, servicing them may require specialized knowledge and equipment, which could pose challenges for some operators.
The Specifications of Pressure Seal Valves
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Pressure Seal Gate Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Butt Weld, Socket Weld |
| Thread Standard | ANSI B1.20.1, BS 21, DIN 2999 |
| Thread Size | 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″, 1-1/4″, 1-1/2″, 2″, etc. |
| Body Material | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Safe for Use With | Oil, Gas, Steam, Water, Chemicals |
| Handle Type | Handwheel, Gear Operated, Actuator |
| Handle Material | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | Up to 2500 psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | Up to 172 bar |
| Operating Pressure | As per application requirements |
The Installation Steps for Pressure Seal Valves
- Preparation: Ensure the work area is clean and free from debris. Gather all necessary tools and equipment for installation.
- Valve Inspection: Inspect the pressure seal valve for any damage or defects before installation. Check for proper valve operation and ensure all components are in good condition.
- Valve Positioning: Position the valve in the desired location within the piping system. Ensure proper alignment with the pipe flanges or connections.
- Flange Preparation: Prepare the flange faces by cleaning them thoroughly to remove any dirt, grease, or debris. Check for any irregularities or damage on the flange surfaces.
- Gasket Installation: Place the appropriate gaskets between the valve flanges and the piping flanges. Ensure the gaskets are properly aligned and seated to provide a tight seal.
- Bolt Installation: Insert the bolts through the bolt holes in the valve flanges and piping flanges. Tighten the bolts evenly using a crisscross pattern to ensure uniform pressure distribution.
- Torqueing: Torque the bolts to the manufacturer’s recommended specifications using a calibrated torque wrench. Follow the recommended torque sequence provided by the manufacturer.
- Leak Testing: Perform a leak test on the installed valve assembly to ensure there are no leaks. Apply pressure gradually and inspect all connections for signs of leakage.
- Final Inspection: Conduct a final inspection of the installed pressure seal valve assembly to ensure it meets all safety and performance requirements.
- Documentation: Document the installation process, including any observations or findings during the installation. Keep records of torque values, pressure tests, and any adjustments made during the installation process.
The Operation Theory of Pressure Seal Valves
- Enhanced Sealing: Pressure Seal Valves feature a unique bonnet design that utilizes pressure from the fluid to enhance sealing integrity. As the internal pressure increases, the pressure from the fluid presses the bonnet against the body, creating a tighter seal.
- Bidirectional Flow Control: These valves can control the flow of fluids in both directions, allowing for efficient operation in various applications.
- High Pressure Capability: Pressure Seal Valves are specifically designed to withstand high-pressure environments, making them ideal for applications where standard valves may fail.
- Reliable Performance: The robust construction and enhanced sealing mechanism of Pressure Seal Valves ensure reliable performance, even under extreme pressure conditions.
The Parameters Chart of Pressure Seal Valves
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Valve Type | Pressure Seal Gate Valve, Pressure Seal Globe Valve, Pressure Seal Check Valve |
| Body Material | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Bonnet Material | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Seal Material | Graphite, Metal, Flexible Graphite |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Stem Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Seat Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Disc Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Connection Type | Flanged, Butt Weld, Socket Weld |
| Pressure Class | 600, 900, 1500, 2500, 4500 PSI |
| Operating Temperature | -29°C to 538°C (-20°F to 1000°F) |
| Sizes Available | 2″ to 24″ (larger sizes available upon request) |
| Compliance Standards | API 600, API 602, API 603, ASME B16.34 |

