What You Need to Know About High Pressure Valve

The Application of High Pressure Valve
Introducing high-pressure valves engineered for demanding industrial applications, Cameron provides a range of solutions, including high pressure relief valves, high pressure solenoid valves, and high pressure ball valves. These valves are crucial components in various industries, ensuring safe and efficient operation under extreme conditions. In oil and gas exploration, high-pressure relief valves safeguard equipment and personnel by releasing excess pressure from pipelines and wellheads. High-pressure solenoid valves play a vital role in controlling fluid flow in hydraulic systems and industrial automation processes, enhancing precision and reliability. Additionally, high-pressure ball valves are utilized in chemical processing plants and power generation facilities to regulate high-pressure fluid and gas flow. With robust construction and advanced technology, Cameron high-pressure valves deliver unparalleled performance and safety in critical industrial applications.
What Are The Types Of High Pressure Valve?
- High Pressure Relief Valve: These valves are designed to automatically release excess pressure from a system to prevent overpressurization, safeguarding equipment and personnel.
- High Pressure Solenoid Valve: Solenoid valves designed to operate under high-pressure conditions, controlling the flow of fluids or gases in hydraulic systems, industrial automation, and other applications.
- High Pressure Ball Valve: Ball valves specifically engineered to withstand high-pressure environments, offering reliable shut-off and flow control in various industrial processes.
- High Pressure Gate Valve: Gate valves capable of handling high-pressure fluids or gases, providing tight shut-off and dependable performance in critical applications.
- High Pressure Globe Valve: Globe valves designed to operate under high-pressure conditions, offering precise flow control and reliable sealing.
What Is High Pressure Valve?
A High Pressure Valve is a type of valve designed to withstand and regulate the flow of fluids or gases under elevated pressure conditions. These valves are specifically engineered to operate effectively and safely in environments where pressures exceed standard operating conditions. High Pressure Valves are crucial components in various industrial applications, including oil and gas exploration, chemical processing, power generation, and hydraulic systems. They are designed with robust materials and construction to ensure reliable performance and prevent leaks or failures under high-pressure conditions. High Pressure Valves play a vital role in maintaining system integrity, controlling flow rates, and ensuring safety in critical industrial processes requiring precise fluid or gas management under elevated pressures.
How Does High Pressure Valve work?
High Pressure Valves operate by controlling the flow of fluids or gases under elevated pressure conditions. When the valve is actuated, the internal mechanism modulates the flow, either allowing fluid to pass through or shutting it off completely. The valve’s robust construction and sealing mechanisms ensure that it can withstand the high pressures without leakage or failure. Depending on the type of valve, such as a high pressure relief valve, high pressure solenoid valve, or high pressure ball valve, the specific operation may vary. However, the fundamental principle remains the same: to regulate fluid or gas flow effectively and safely under high-pressure environments.
Features of High Pressure Valve
- Robust Construction: High Pressure Valves are built with durable materials such as stainless steel, alloy steel, or hardened alloys, ensuring they can withstand extreme pressure environments without failure.
- High Pressure Rating: These valves are designed to handle high-pressure fluids or gases, with pressure ratings typically exceeding standard valves.
- Reliable Sealing: They feature advanced sealing mechanisms such as metal-to-metal seals or resilient seals to ensure leak-tight operation even under high-pressure conditions.
- Precise Flow Control: High Pressure Valves offer precise control over fluid or gas flow rates, allowing for accurate regulation of processes in critical applications.
- Versatile Applications: They find applications in various industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and hydraulic systems, where precise fluid or gas management under high-pressure conditions is essential.
- Safety Features: Many High Pressure Valves are equipped with safety features such as pressure relief mechanisms or fail-safe designs to prevent overpressurization and ensure personnel and equipment safety.
- Corrosion Resistance: Some valves are designed with corrosion-resistant materials or coatings to withstand corrosive environments often found in high-pressure applications.
Advantages of High Pressure Valve
- Safe Operation: High Pressure Valves ensure safe handling of fluids or gases under elevated pressure conditions, preventing overpressurization and potential hazards to personnel and equipment.
- Reliable Performance: These valves offer reliable performance even in demanding high-pressure environments, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous operation of industrial processes.
- Precise Control: High Pressure Valves provide precise control over fluid or gas flow rates, allowing for accurate regulation and optimization of processes to meet specific requirements.
- Versatility: They are suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and hydraulic systems, demonstrating their versatility and adaptability.
- Durable Construction: High Pressure Valves are constructed with robust materials and engineering designs to withstand extreme pressure conditions, ensuring long-term durability and reliability.
- Efficient Flow Management: These valves facilitate efficient flow management, reducing energy consumption and optimizing system performance in high-pressure applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Despite their initial investment, High Pressure Valves offer long-term cost savings by minimizing maintenance requirements, reducing downtime, and improving overall process efficiency.
- Compliance: Many High Pressure Valves are designed to meet industry standards and regulations, ensuring compliance with safety and performance requirements in critical applications.
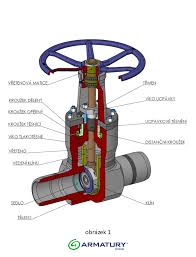
The Specifications of High Pressure Valve
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | High Pressure Valve |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Hardened Alloys |
| Attachment Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, Clamp, Socket Weld |
| Thread Standard | ANSI, DIN, JIS, BS, ISO |
| Thread Size | 1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″, 1-1/4″, 1-1/2″, 2″ |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Oil, Gas, Chemicals, Steam, Cryogenic |
| Handle Type | Lever, Gear, Actuator |
| Handle Material | Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | Varies based on size and design, e.g., 1000 psi |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | Varies based on size and design, e.g., 70 bar |
| Operating Pressure | Varies based on application requirements |
The Installation Steps for High Pressure Valve
- Type: High Pressure Valve
- Ball Material: Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Hardened Alloys
- Attachment Type: Flanged, Threaded, Welded, Clamp, Socket Weld
- Thread Standard: ANSI, DIN, JIS, BS, ISO
- Thread Size: 1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″, 1-1/4″, 1-1/2″, 2″
- Body Material: Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel
- Safe for Use With: Water, Oil, Gas, Chemicals, Steam, Cryogenic
- Handle Type: Lever, Gear, Actuator
- Handle Material: Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel
- Maximum Working Pressure (psi): Varies based on size and design, e.g., 1000 psi
- Maximum Working Pressure (bar): Varies based on size and design, e.g., 70 bar
- Operating Pressure: Varies based on application requirements
The Operation Theory of High Pressure Valve
- Prepare the Work Area: Ensure the work area is clean, dry, and free from debris or contaminants that could affect the valve’s performance.
- Inspect the Valve: Check the High Pressure Valve for any damage or defects before installation, including scratches, dents, or leaks.
- Prepare the Pipeline: Cut and prepare the pipeline according to the valve’s specifications, ensuring proper alignment and clearance for installation.
- Apply Thread Sealant: If the valve has threaded connections, apply a suitable thread sealant or tape to ensure a leak-tight seal.
- Install the Valve: Position the High Pressure Valve in the pipeline, ensuring it is aligned correctly with the flow direction indicated by the arrow on the valve body.
- Tighten Connections: Use appropriate tools to tighten the valve connections securely, ensuring they are snug but not over-tightened to avoid damage.
- Pressure Test: Conduct a pressure test to verify the integrity of the installation and ensure there are no leaks or defects.
- Secure the Valve: Once the pressure test is successful, secure the valve in place using suitable mounting hardware or brackets to prevent movement or vibration.
- Final Inspection: Perform a final visual inspection of the installation to ensure everything is correctly aligned, tightened, and secure.
- Document Installation: Document the installation details, including valve specifications, installation date, and any test results, for future reference and maintenance purposes.
The Parameters Table of High Pressure Valve
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | High Pressure Valve |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Hardened Alloys |
| Seat Material | PTFE, Reinforced PTFE, PEEK, Metal |
| Stem Material | Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Hardened Alloys |
| Connection Type | Flanged, Threaded, Welded, Clamp, Socket Weld |
| Thread Standard | ANSI, DIN, JIS, BS, ISO |
| Thread Size | 1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″, 1-1/4″, 1-1/2″, 2″ |
| Safe for Use With | Water, Oil, Gas, Chemicals, Steam, Cryogenic |
| Maximum Working Pressure (psi) | Varies based on size and design |
| Maximum Working Pressure (bar) | Varies based on size and design |
| Operating Pressure | Varies based on application requirements |